|
PACK CARBURISING |
Pack
carburization is the oldest method among the case hardening treatments
and sufficient attempts has not been made to understand this process in
terms of heat and mass transfer, effect of alloying elements,
dimensions of the sample, etc. Thus, a two dimensional mathematical
model in cylindrical co-ordinate is developed for simulating pack
carburization process for chromium bearing steel (a ternary system
(Fe-C-Cr)) in this study. Heat and mass balance equations are solved
simultaneously where surface temperature of the sample varies with
time, but the carbon potential at the surface during the process
remains constant. Fully implicit finite volume technique is used to
solve the governing equations. A good agreement has been found between
the predicted and published data.
It is observed
that two dimension analysis gives better description of the process
than one dimension. It is found that the effect of second dimension on
the craburising process is significant especially in predicting the
case depth near the corners of the sample. Neglecting the second
dimension in modeling and subsequently analysis of the results on case
depth may provide wrong interpretation and thus may affect the
operating life of the specimen. Sensitivity analysis shows that as the
size of the sample increases the case depth is decreased and thin layer
of charcoal packing increases the case depth. |
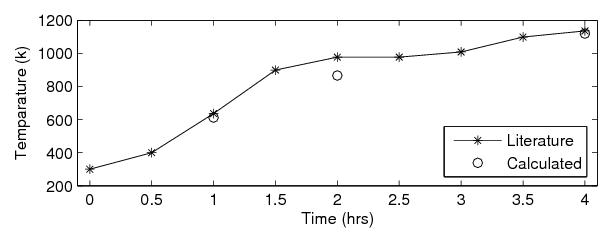 Figure 1. Comparison between computed and published expt. temperature data. |
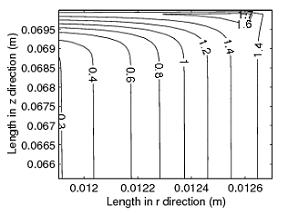 Figure 2. Computed carbon concentration profile within the specimen (high C concn. at the corner is evident). 2D pack carburizing at 1173 K for 6 hours. |
| For further details or queries or publication related to this, kindly contact us at the address given on the web-site. |