Development of Heap Leaching using Discrete Liquid Flow Theory for Multi-particle System
HEAP LEACHING
Heap leaching is being studied with renewed interest as metal content in many ores has decreased worldwide. Moreover, it is more economical and environmentally friendly than other extraction routes of metals, such as pyrometallurgy.
Heap leaching is one of those processes where liquid flows in rivulet and droplet form. In heap leaching, lean ore such as Cu, Ni and U are used to extract the metal.
In the present study, the liquid flow behaviour is studied in a heap in terms of:
- Tortuosity
- Liquid distribution
- Contact angle
- Various sizes of particles
- Simultaneous irrigation of the bed with multiple inlets
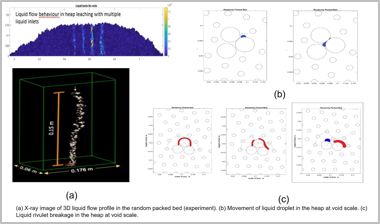
The novelty of this work is that it captures the correct nature of the liquid flow (which is discrete) in a random heap leaching bed deterministically, which has been lacking until now. Discrete Element Method (DEM), which is an effective tool to simulate granular materials, is used to pack a 2D vertical heap, as shown in Fig 1.
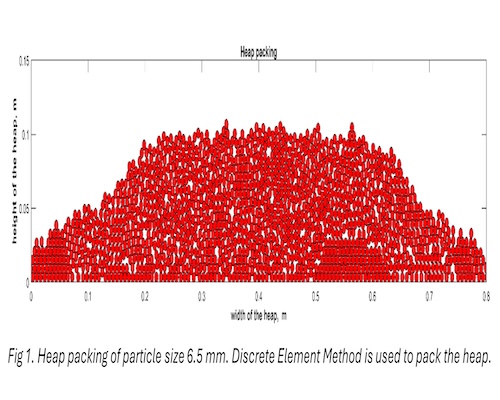
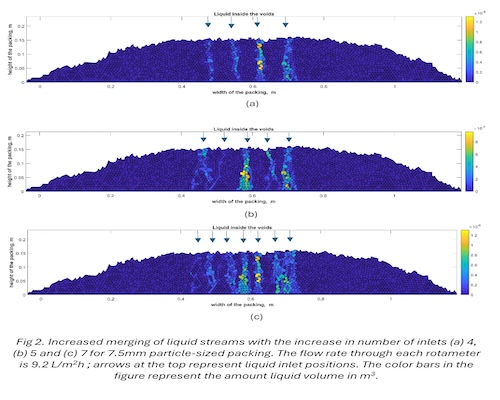
Fig 2 shows that the merging of liquid streams increases when the number of liquid inlets increases, reducing the potential area of the bed that can be exposed to the liquid. The merging of the liquid streams is more prominent towards the bottom of the packing as compared to the top. The liquid disperses or spreads as it descends the bed merging with the neighbouring liquid streams.
For further details, queries, or publications related to this research, please contact us through our contact information on the website.